RSPAN copies all the traffic that comes in and out of source ports or source VLANs to a destination port on a different switch for analysis. RSPAN does not affect the switching of traffic on the source ports or VLANs that are being used.
This blog post shows an example of mirroring all the traffic from a server to a workstation connected to a different switch.
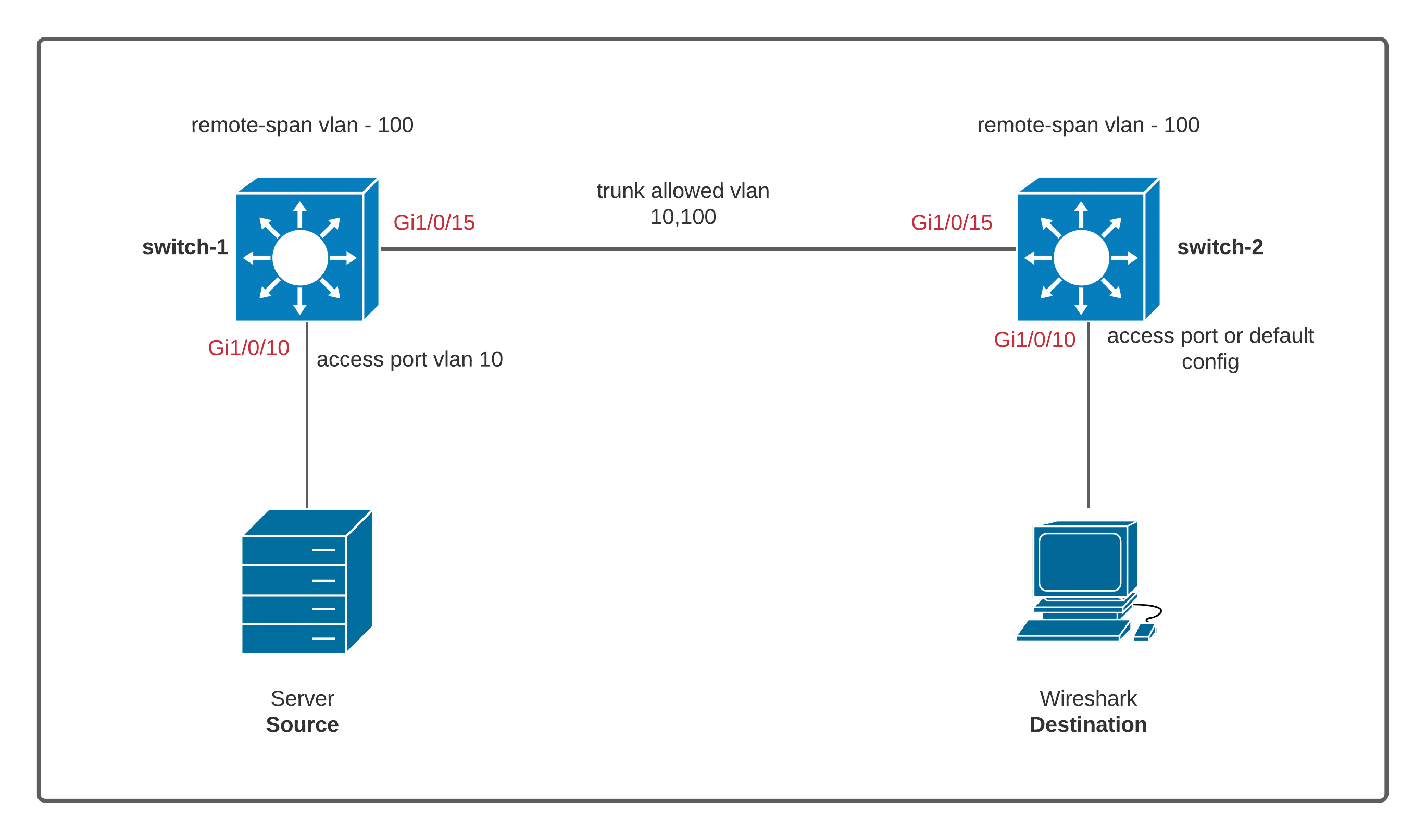
Diagram
Configuration
It is recommended to configure an RSPAN VLAN before you configure an RSPAN source or a destination session.
switch-1
--------
vlan 100
name RSPAN-VLAN
remote-span
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/10
description SERVER-1
switchport access vlan 10
switchport mode access
spanning-tree portfast
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/15
description TRUNK-TO-SWITCH-2
switchport trunk allowed vlan 10,100
switchport mode trunk
monitor session 10 source interface gi1/0/10
monitor session 10 destination remote vlan 100switch-1 configuration
switch-2
--------
vlan 100
name RSPAN-VLAN
remote-span
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/10
description WIRESHARK
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/15
description TRUNK-TO-SWITCH-1
switchport trunk allowed vlan 10,100
switchport mode trunk
monitor session 10 source remote vlan 100
monitor session 10 destination interface gi1/0/10switch-2 configuration
That's all, now Wireshark should be able to capture all the traffic that comes in and out of the server port.
Local SPAN configuration example
SPAN copies all the traffic that comes in and out of source ports or source VLANs to a destination port on the same switch for analysis.
Suppose you want to mirror all the traffic from port Gi1/0/10 to Gi1/0/48 on the same switch.
monitor session 10 source interface gi1/0/10 both
monitor session 10 destination interface gi1/0/48Reference