In the previous articles, we have discussed about PIM Dense Mode and PIM Sparse Mode. Both protocols use IGMPv2 and known as Any Source Multicast (ASM). You can check out both articles below:
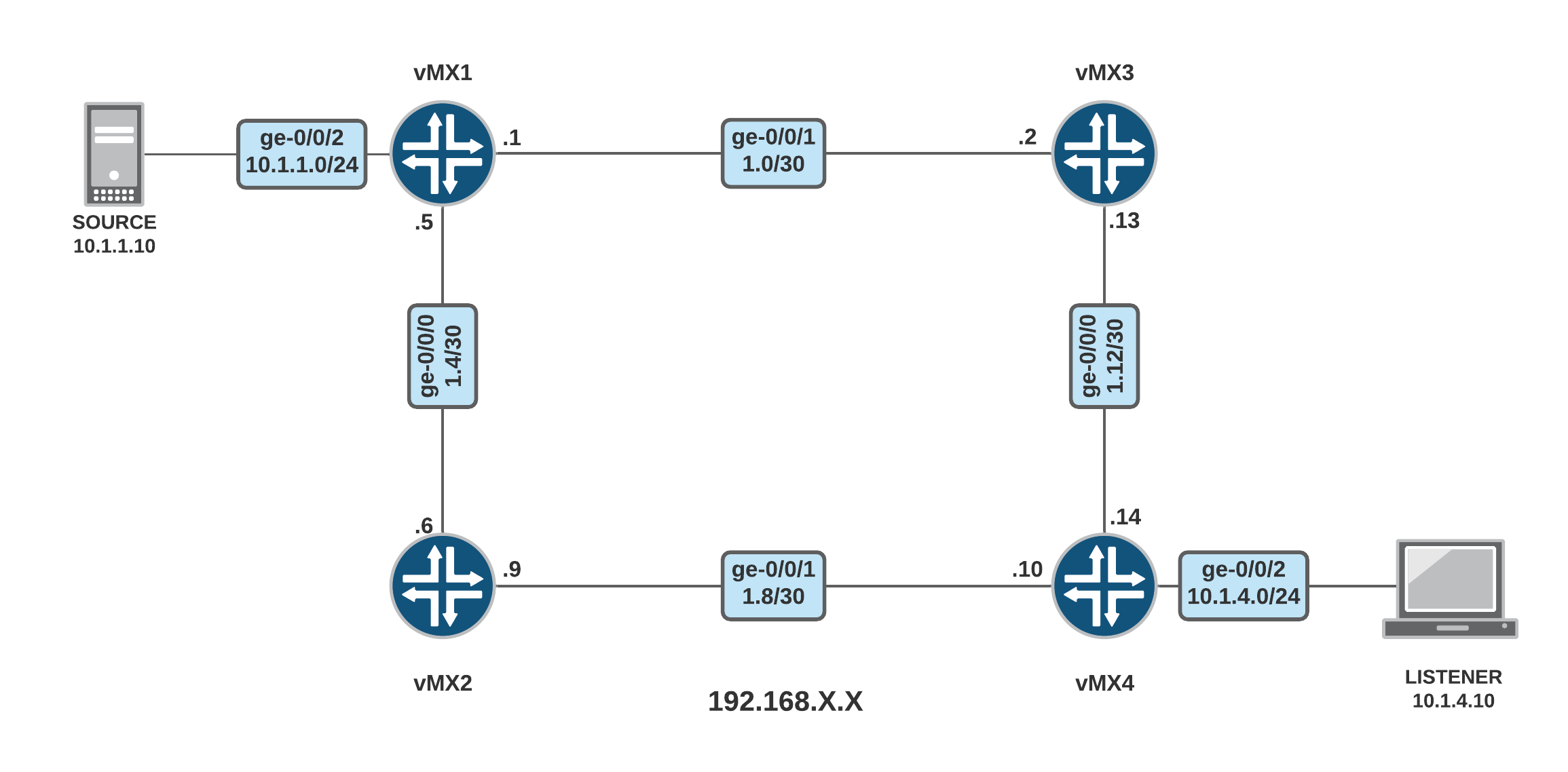
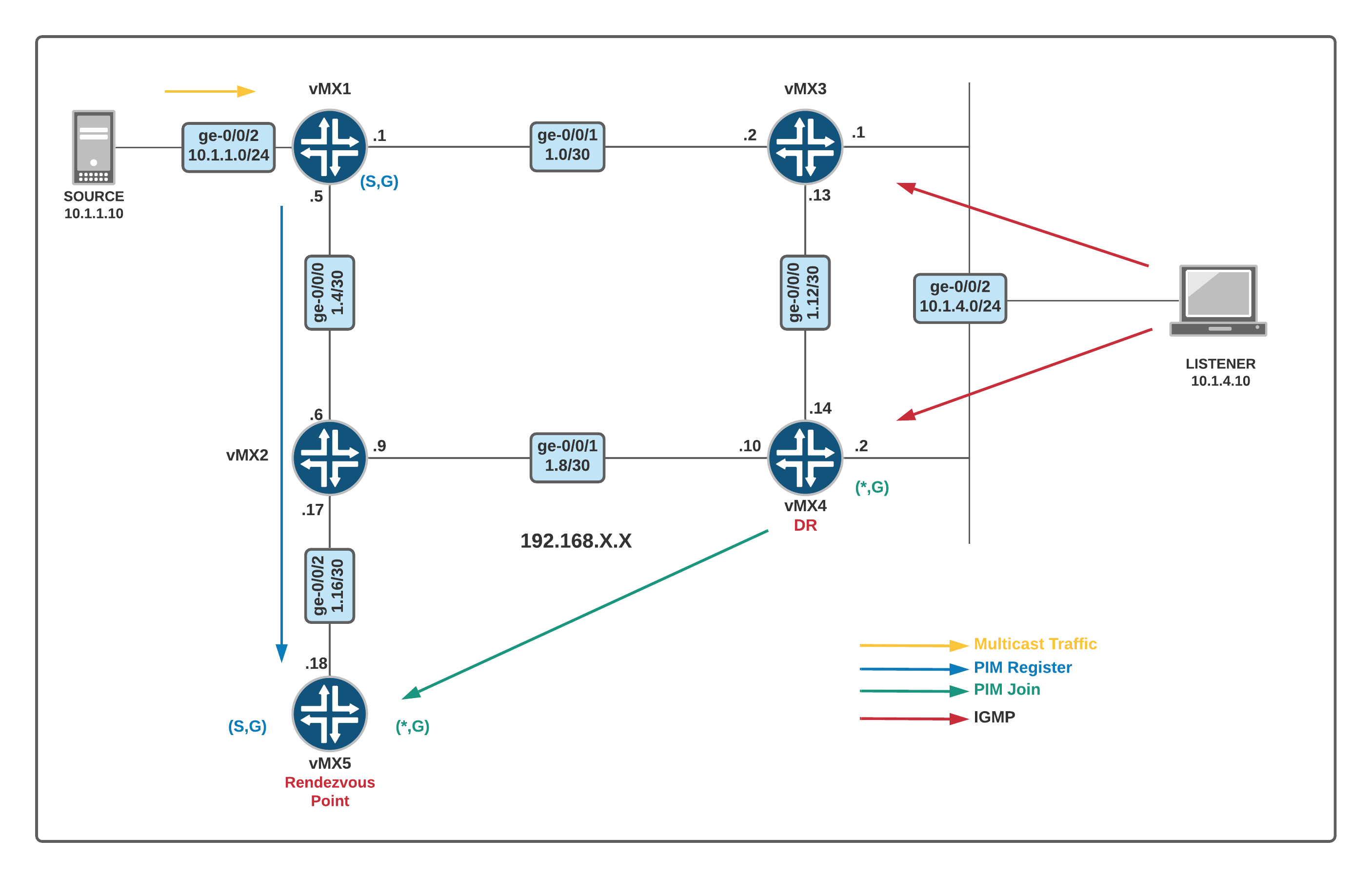
Source Specific Multicast
PIM SSM uses a subset of PIM sparse mode and IGMPv3 to allow a client to receive multicast traffic directly from the source.
PIM SSM uses the PIM sparse mode functionality to create Shortest Path Tree (SPT) between the receiver and the source without the help of RP.
An SSM-configured network has distinct advantages over a traditionally configured PIM sparse-mode network. There is no need for shared trees or RP routers. PIM SSM is simpler than PIM sparse mode because only the one-to-many model is supported.
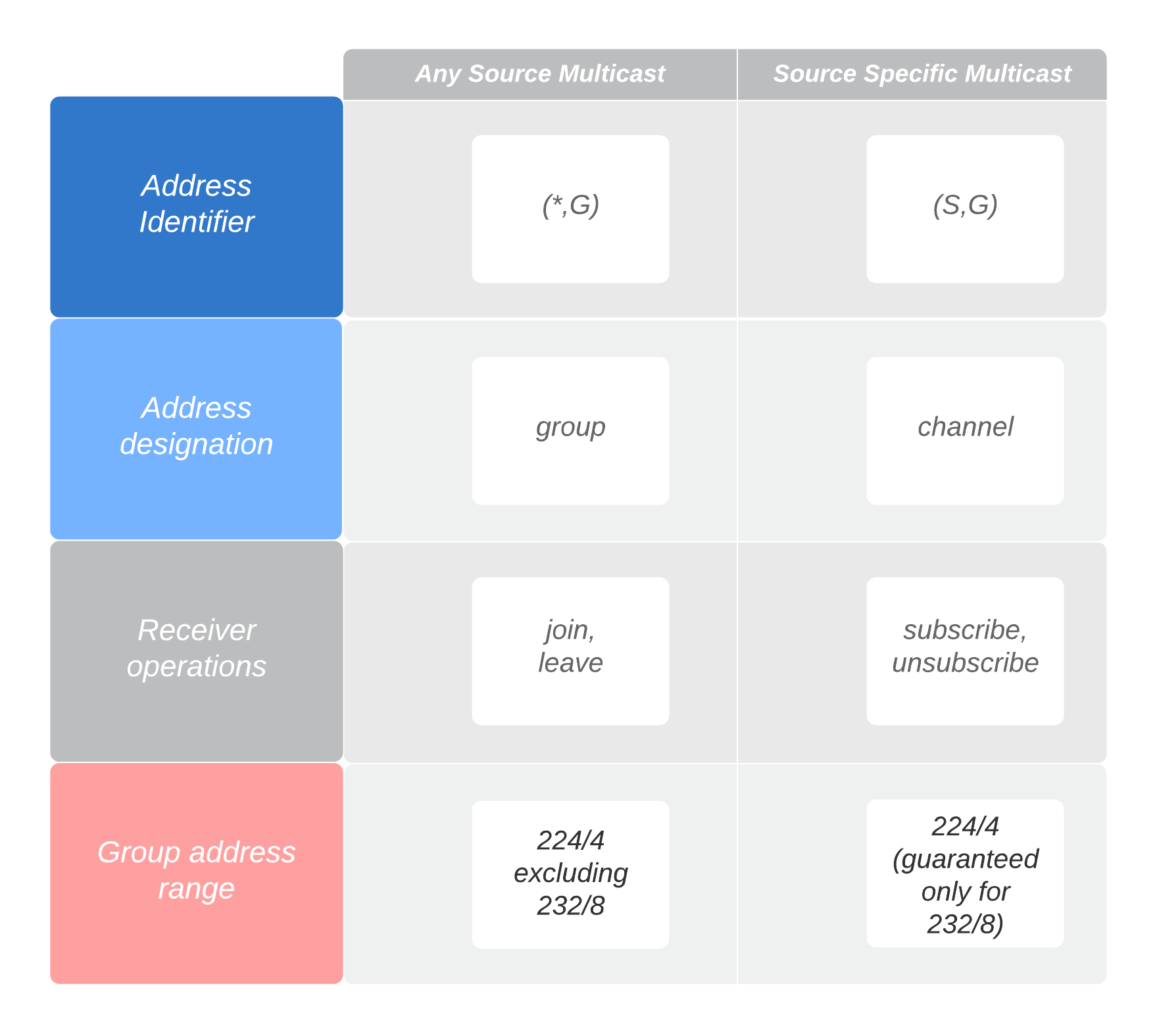
By default, the SSM group multicast address is limited to the IP address range from 232.0.0.0 through 232.255.255.255. However, you can extend SSM operations into another Class D range by making a configuration change.
How PIM SSM works
- A host subscribes to a SSM channel (by means of IGMPv3), announcing a desire to join group G and source S.
- The directly connected PIM sparse-mode router sends an (S,G) join message to its RPF PIM neighbor for the source.
- The (S,G) join message initiates the source tree and then builds it out hop-by-hop until it reaches the source.
- Using the source tree, multicast traffic is delivered to the subscribing host.
SSM Configuration and Verification
Diagram and Configuration
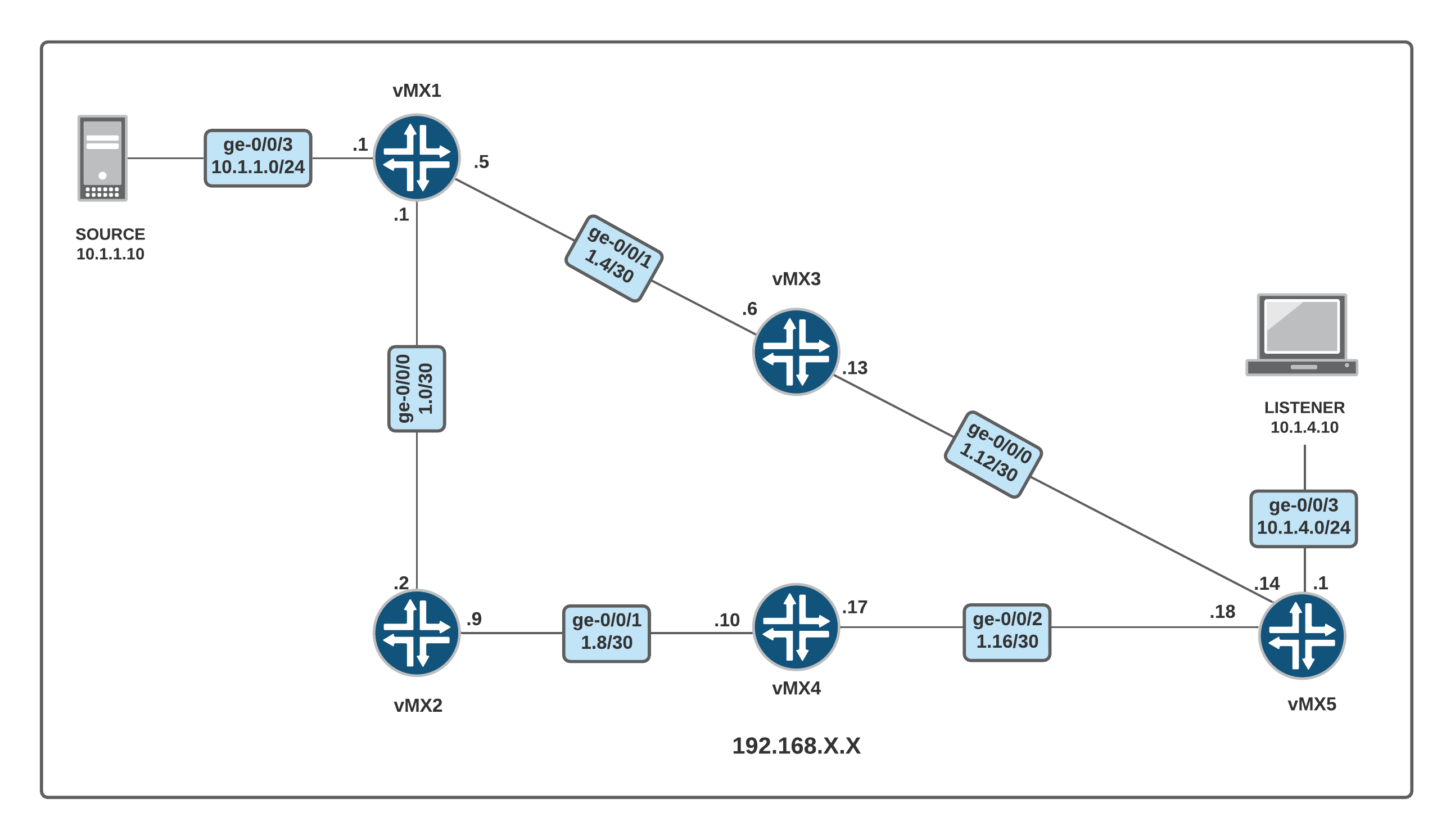
set system host-name vMX1
set interfaces ge-0/0/0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.1.1/30
set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.1.5/30
set interfaces ge-0/0/3 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.1.1/24
set protocols igmp interface ge-0/0/3.0 version 3
set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-0/0/0.0
set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-0/0/1.0
set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-0/0/3.0
set protocols pim interface ge-0/0/0.0 mode sparse
set protocols pim interface ge-0/0/1.0 mode sparse
set system host-name vMX2
set interfaces ge-0/0/0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.1.2/30
set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.1.9/30
set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-0/0/0.0
set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-0/0/1.0
set protocols pim interface ge-0/0/0.0 mode sparse
set protocols pim interface ge-0/0/1.0 mode sparse
set system host-name vMX3
set interfaces ge-0/0/0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.1.13/30
set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.1.6/30
set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-0/0/0.0
set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-0/0/1.0
set protocols pim interface ge-0/0/0.0 mode sparse
set protocols pim interface ge-0/0/1.0 mode sparse
set system host-name vMX4
set interfaces ge-0/0/1 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.1.10/30
set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.1.17/30
set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-0/0/1.0
set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-0/0/2.0
set protocols pim interface ge-0/0/1.0 mode sparse
set protocols pim interface ge-0/0/2.0 mode sparse
set system host-name vMX5
set interfaces ge-0/0/0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.1.14/30
set interfaces ge-0/0/2 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.1.18/30
set interfaces ge-0/0/3 unit 0 family inet address 10.1.4.1/24
set protocols igmp interface ge-0/0/3.0 version 3
set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-0/0/0.0
set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-0/0/2.0
set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-0/0/3.0
set protocols pim interface ge-0/0/0.0 mode sparse
set protocols pim interface ge-0/0/2.0 mode sparse
set protocols pim interface ge-0/0/3.0 mode sparseLet's configure the LISTENERto subscribe the multicast channel 232.1.1.1
LISTENER
--------
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
ip address 10.1.4.10 255.255.255.0
ip igmp version 3
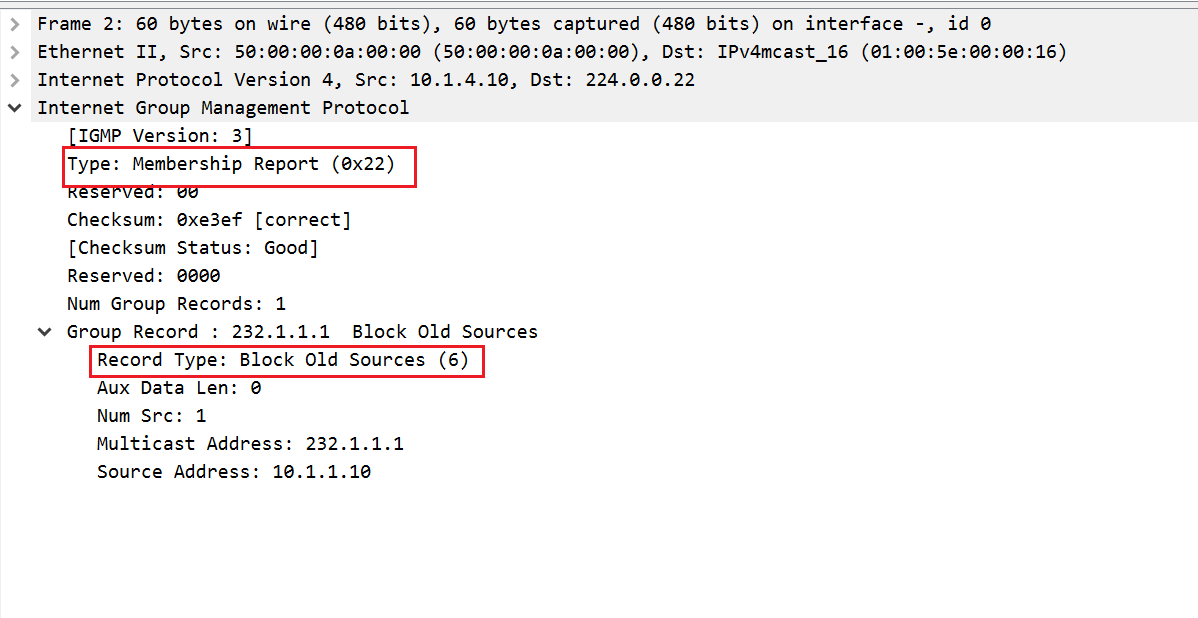
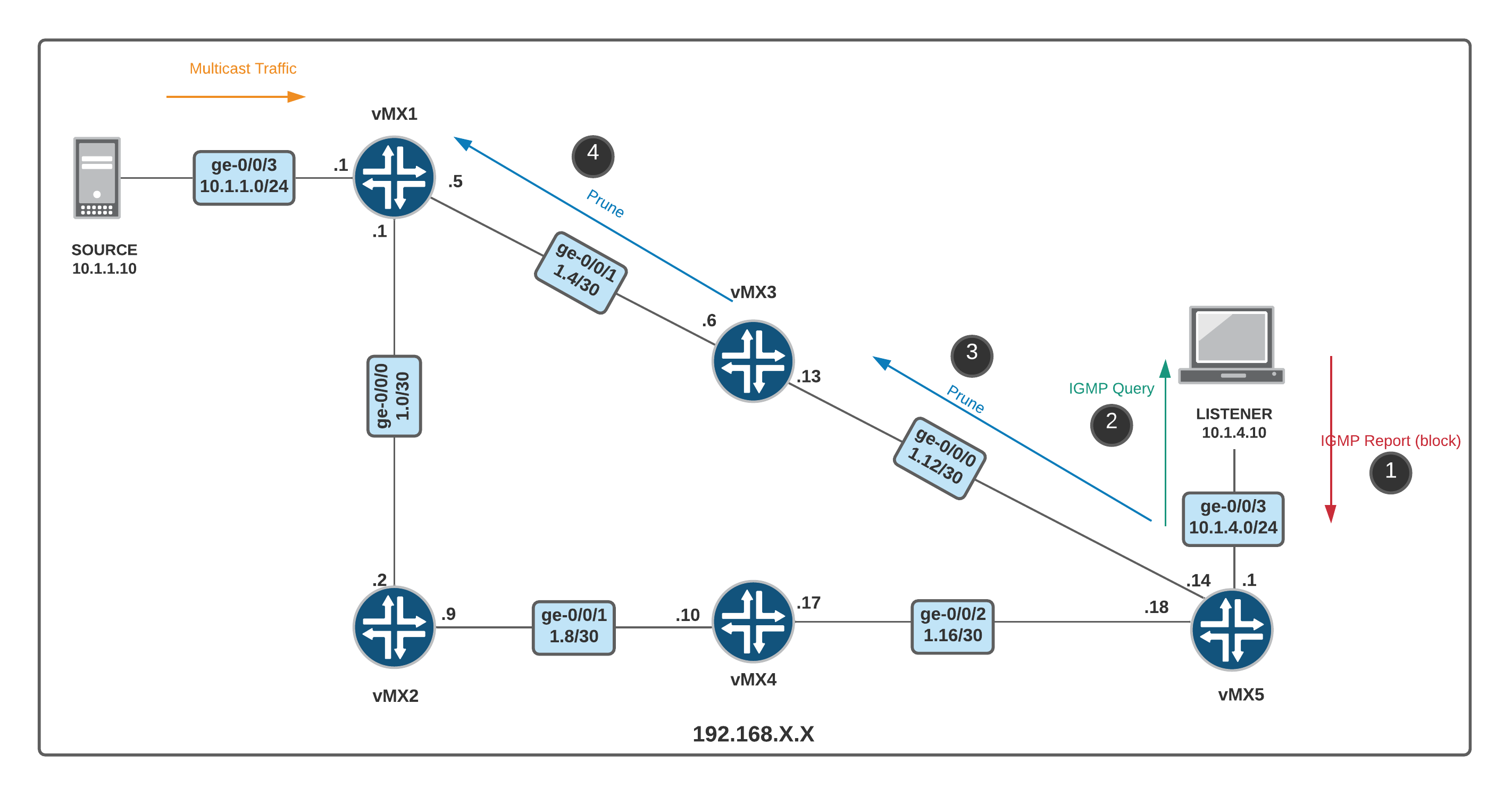
igmp join-group 232.1.1.1 source 10.1.1.10- LISTENER sends IGMP report to the multicast address of 224.0.0.22 which is used by IGMPv3. We can see that the version is 3 and type is Membership Report.
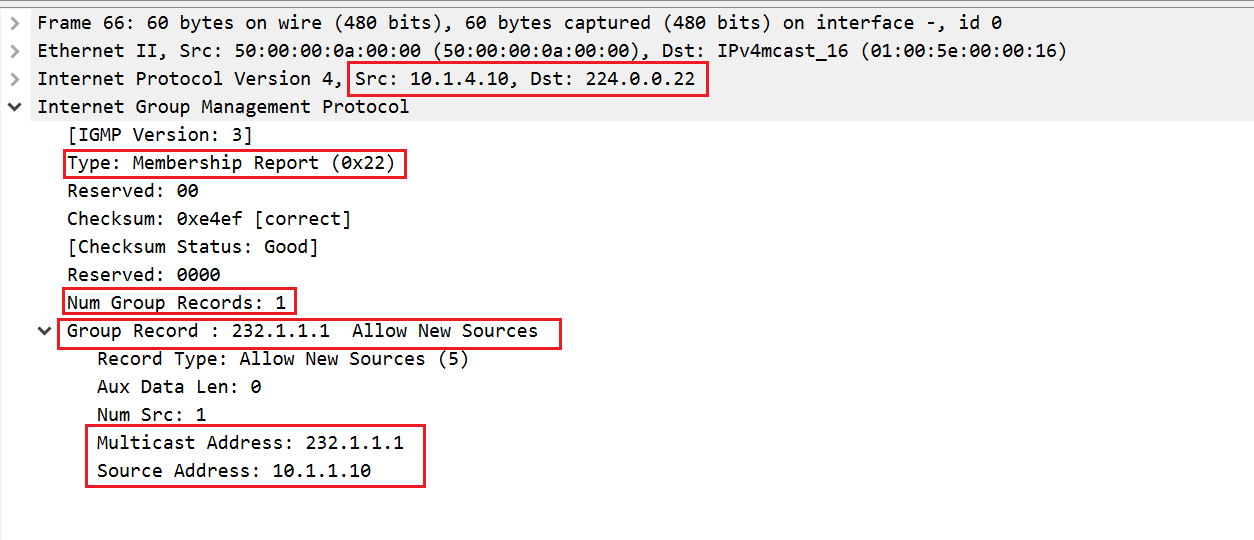
2. vMX5 sends PIM Join message to vMX3 towrds the SOURCE (10.1.1.10) vMX3 then sends another PIM Join message to vMX1.
Why doesn't it send it to vMX4? Well, the shortest path to reach the SOURCE is via vMX3. We can use mtrace command to verify the path from LISTENER to SOURCE.
root@vMX5> mtrace 10.1.1.10
mtrace: WARNING: no multicast group specified, so no statistics printed
Mtrace from 10.1.1.10 to 192.168.1.14 via group 0.0.0.0
Querying full reverse path... * *
0 ? (192.168.1.14)
-1 ? (192.168.1.13) PIM thresh^ 1
-2 ? (192.168.1.5) PIM thresh^ 1
-3 ? (10.1.1.10)
Round trip time 549 ms; total ttl of 2 required.
Please note that this is (S,G) Join
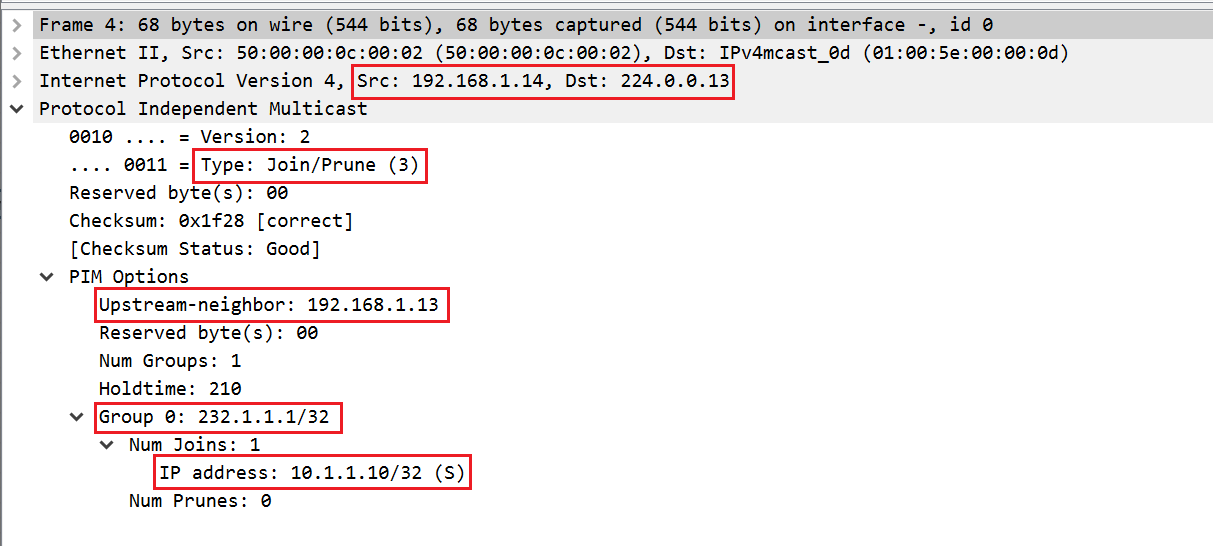
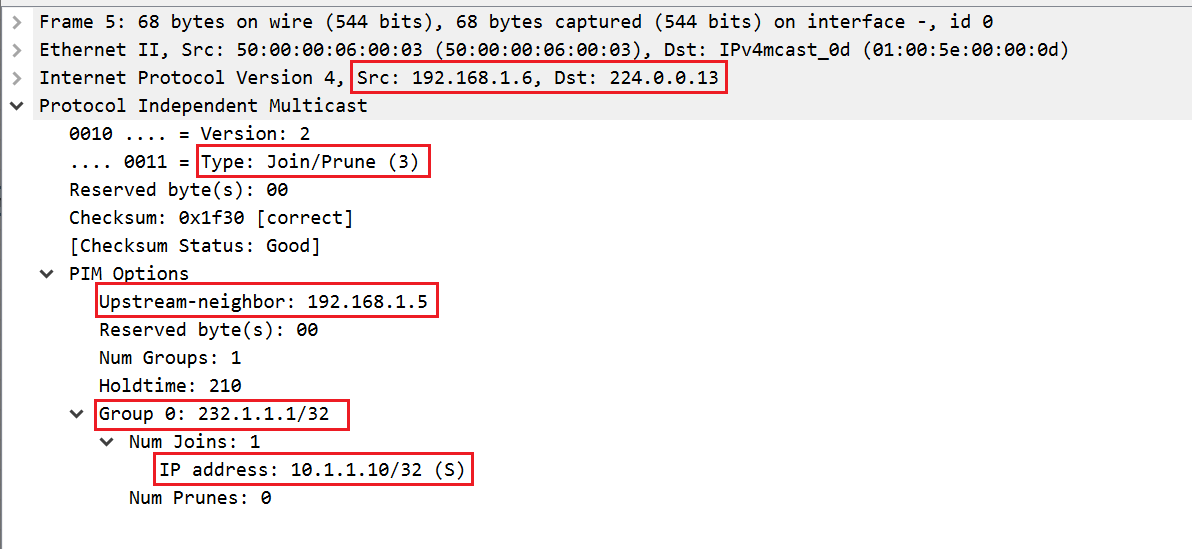
Let's check the CLI output hop-by-hop from vMX5 >> vMX3 >> vMX1
vMX5
----
root@vMX5> show pim join extensive
Instance: PIM.master Family: INET
R = Rendezvous Point Tree, S = Sparse, W = Wildcard
Group: 232.1.1.1 <<< G
Source: 10.1.1.10 <<< S
Flags: sparse,spt
Upstream interface: ge-0/0/0.0 <<< Towards Source
Upstream neighbor: 192.168.1.13 <<< Upstream PIM Neighbor
Upstream state: Join to Source
Keepalive timeout: 279
Uptime: 00:01:21
Downstream neighbors:
Interface: Pseudo-GMP
ge-0/0/3.0 <<< Towards Listener
Number of downstream interfaces: 1
Number of downstream neighbors: 0
vMX3
----
Group: 232.1.1.1
Source: 10.1.1.10
Flags: sparse,spt
Upstream interface: ge-0/0/1.0
Upstream neighbor: 192.168.1.5
Upstream state: Join to Source
Keepalive timeout: 257
Uptime: 00:01:43
Downstream neighbors:
Interface: ge-0/0/0.0
192.168.1.14 State: Join Flags: S Timeout: 166
Uptime: 00:01:43 Time since last Join: 00:00:44
Number of downstream interfaces: 1
Number of downstream neighbors: 1
vMX1
----
root@vMX1> show pim join extensive
Instance: PIM.master Family: INET
R = Rendezvous Point Tree, S = Sparse, W = Wildcard
Group: 232.1.1.1
Source: 10.1.1.10
Flags: sparse,spt
Upstream interface: ge-0/0/3.0
Upstream neighbor: Direct <<< SOURCE is directly connected
Upstream state: Local Source
Keepalive timeout:
Uptime: 00:01:46
Downstream neighbors: <<< Downstream PIM neighor
Interface: ge-0/0/1.0
192.168.1.6 State: Join Flags: S Timeout: 164
Uptime: 00:01:46 Time since last Join: 00:00:46
Number of downstream interfaces: 1
Number of downstream neighbors: 1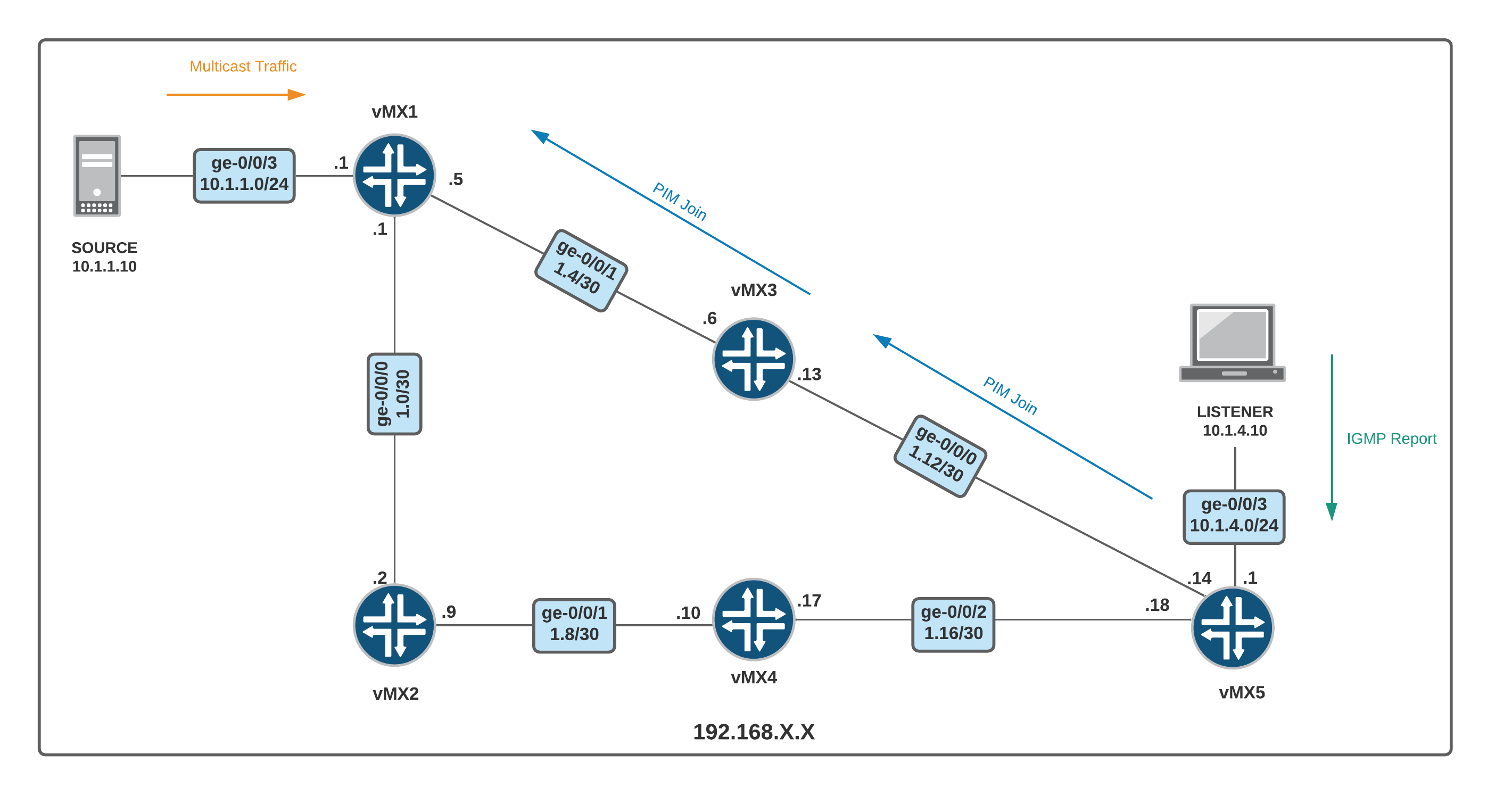
3. Let's unsubscribe from 232.1.1.1 channel and check the packet captures.
LISTENER
--------
LISTENER(config-if)#no ip igmp join-group 232.1.1.1 source 10.1.1.10IGMP Report/Query message is used between LISTENER and LHR.
- LISTENER sends IGMP Report message type
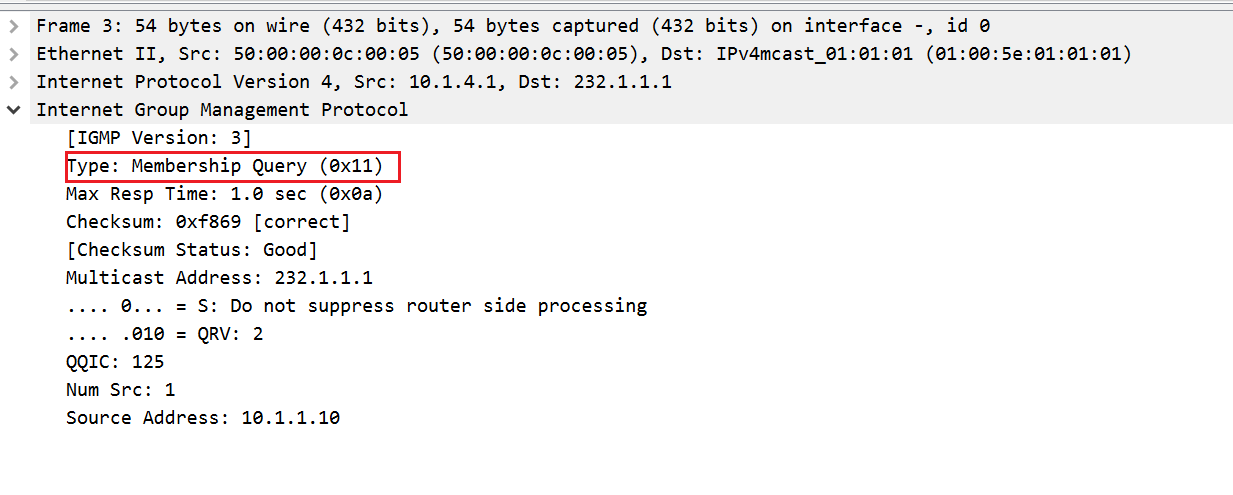
Block Old Sourcesto let the LHR know that it doesn't want to receive the multicast traffic anymore. - And then the LHR sends Membership Query to check if there is any other listener on the segment.
- If no one replies, it will send PIM Prune message towards the upstream neighbor.
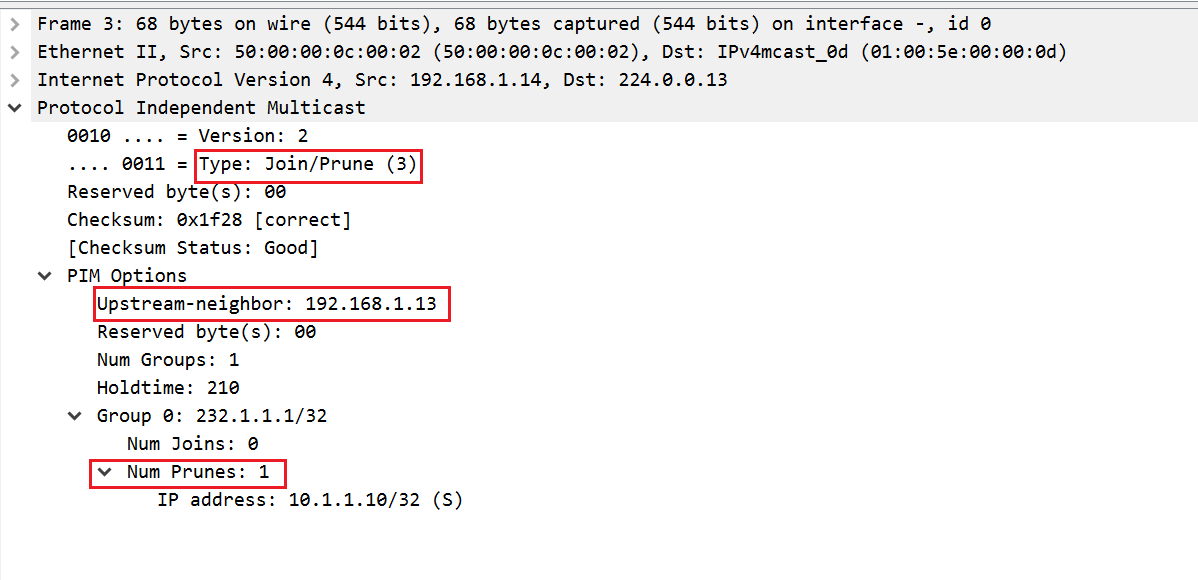
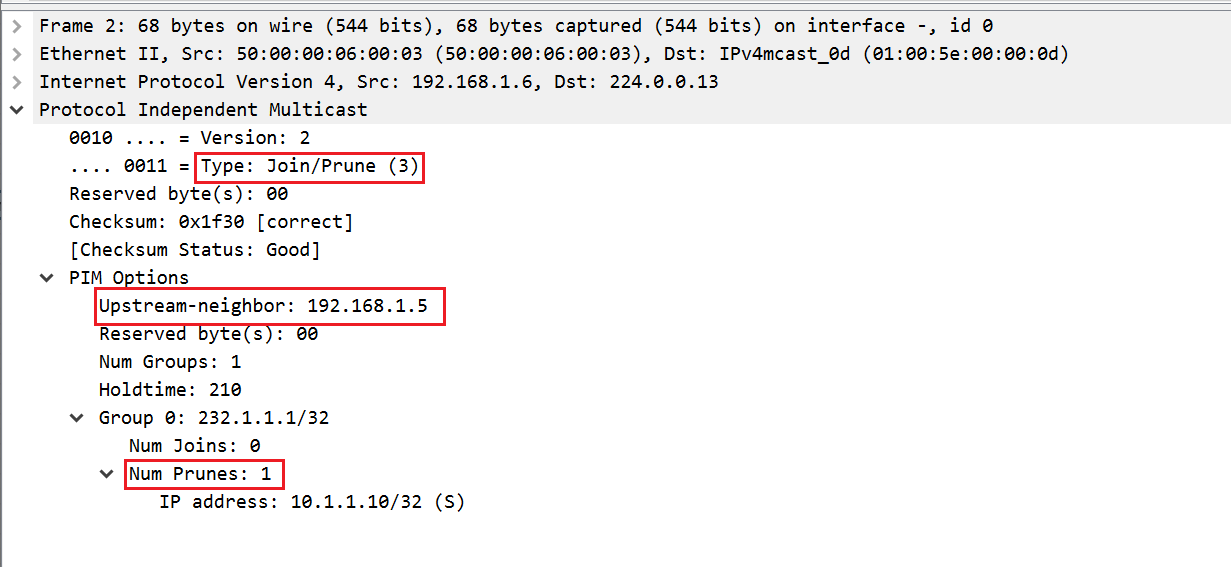
PIM Prune message should go from vMX5 > vMX3 > vMX1. Let's check it out.
Reference

Thanks for reading.
As always, your feedback and comments are more than welcome.







